The clues that the doctor uses are the levels of white cells protein and glucose in the CSF. Typically in bacterial meningitis the white cell count is much higher than in viral meningitis and is a different type of white cell the protein is much higher and the glucose is much lower than in viral meningitis.
110 of serum level.
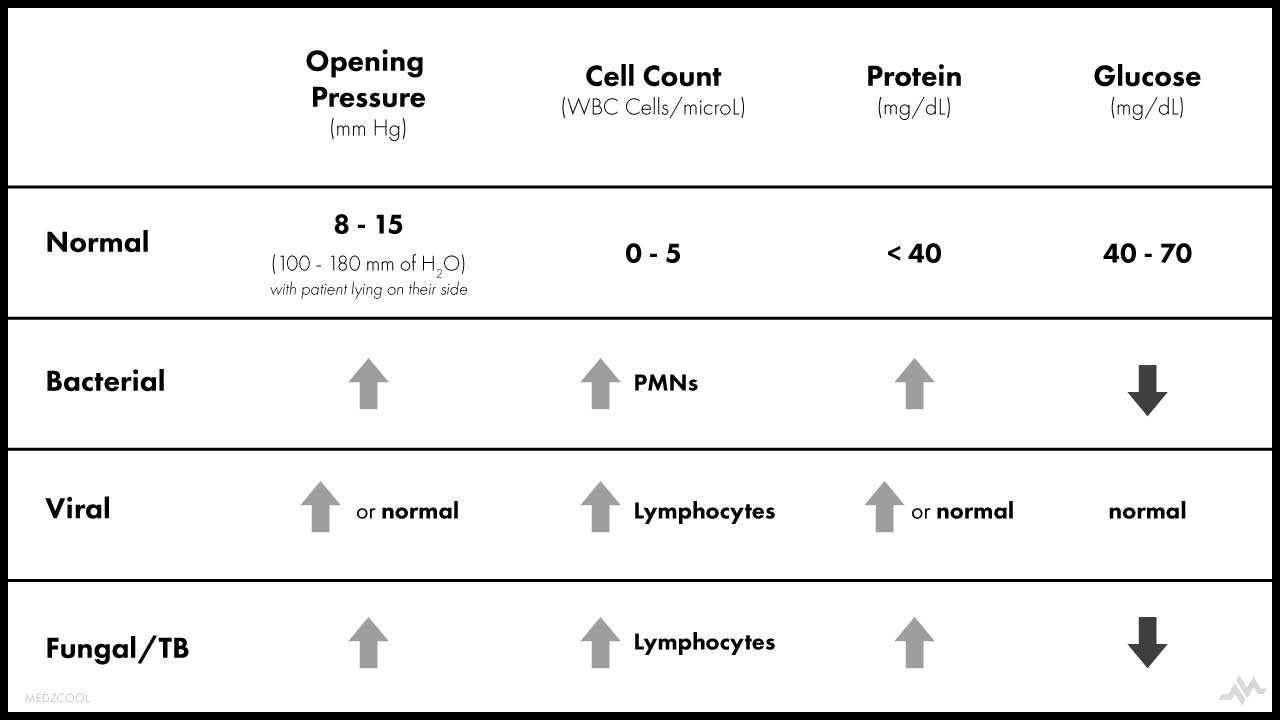
Bacterial vs viral meningitis csf. This was a retrospectively derived n819 and prospectively validated n190 score to distinguish bacterial from viral meningitis in children 29 days to 14 years of age in 25 Spanish EDs. Based on clinical symptoms viral meningitis cannot be reliably differentiated from bacterial meningitis although viral meningitis typically follows a more benign clinical course. However a comparable group of children with viral meningitis did not have similar elevations in serum CRP ie 50-150 in bacterial meningitis group vs 20 in the viral meningitis group.
At an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 097 our model represented by the equation. For such cases additional non-microbiological tests may be helpful. CSF analysis typically reveals neutrophilic pleocytosis elevated protein level and a low glucose level.
Tb bacterial viral. Oligoclonal bands in multiple sclerosis. One of many studies showed higher CSF protein level in bacterial meningitis than viral meningitis with mean 6410142852 vs.
Increased in GBS vasculitis and sarcoidosis. The model fit the data well Hosmer-Lemeshow statistic. Bacterial meningitis is an acute inflammation of the meninges caused by bacteria.
Viral Meningitis is not that severe and the patient usually recovers in a time span of 10 days. In most cases differentiating viral from bacterial meningitis is relatively easy based on clinical examination CSF appearance and results of CSF examination cytology biochemistry and Gram stain. Viral meningitis can be established.
50180 mmH 2 O Glucose. Bacterial meningitis has a poor prognosis while viral meningitis is self limiting has a good prognosis and no long term sequelae. However in about 20 of cases this diagnosis may be difficult.
Log odds of bacterial meningitis 0343 - 0003 TNC - 34802 TP 21991 TP - 0345 AGE was highly accurate when differentiating between bacterial and enteroviral meningitis. Increased in CNS inflammation including CSF drains and blood in CSF GLUCOSE. Normal values CSF.
Viral meningitis has no evidence of bacteria present in cerebral spinal fluid CSF. In Streptococcus-mediated meningitis. Patients with bacterial meningitis usually present with the sudden onset of headache fever nuchal rigidity and photophobia.
Upon lumbar puncture CSF looks turbid in bacterial meningitis while it looks clear in viral meningitis. There are various differences between bacterial and viral meningitis. Table 2 summarizes the most common CSF findings associated with.
At probability cutoffs between 01 and 04 the. This is certainly not the case when one is suffering from bacterial meningitis. There are two main types of meningitis depending on the causative agent bacterial and viral meningitis.
In the derivation cohort they found the following predictors were best and gave them a weighted score dubbed the Meningitis Score for Emergencies MSE. Gram stain may be negative in up to 60 of cases of bacterial meningitis even without prior antibiotics A predominance of lymphocytes does not exclude bacterial meningitis Neutrophils may predominate in viral meningitis even after the first 24 hours If the CSF is abnormal the safest course is to treat for bacterial meningitis. A lumbar puncture is the usual procedure performed from which a diagnosis of bacterial vs.
Less than half serum in infections bacterial Tb and fungal infections and vasculitis and sarcoidosis. Increased in infection. It can be caused by Streptococcus pneumonia Neisseria meningitides Haemophilus influenzae etc.
Less than 35 mgdL. Characteristic findings in bacterial meningitis include a CSF glucose concentration CSF to serum glucose ratio of 04 a protein concentration 200 mgdL and a white blood cell count above 1000microL usually composed primarily of neutrophils 2811. The first one is intensity.
CNS infections can cause lowered CSF glucose levels although glucose levels are usually normal in viral infections Table 2. 91744468 mgdl 9 11. CSF obtained from the lumbar puncture is examined directly and cultured and the results of these analyses are critical to diagnose either bacterial or viral meningitis.
Normally at least 75 serum glucose. Viral meningitis is typically characterized by an elevated CSF white blood cell count with a predominance of lymphocytes and increased protein level. 14 Normal glucose levels do not rule out infection because up to 50.
Halaman
Health Navigator NZ
Cari Blog Ini
Arsip Blog
Arsip Blog
Label
- 13th
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- aaliyah
- abdomen
- abdominal
- abortion
- about
- absent
- accupuncture
- ache
- acid
- acne
- action
- activities
- activity
- acupuncture
- addicted
- aden
- adopt
- adopting
- adoption
- adults
- advanced
- advice
- afford
- africa
- after
- agency
- airplane
- alana
- album
- allergies
- allergy
- alone
- along
- alternatives
- amazon
- america
- american
- amniotic
- anais
- anatomically
- angel
- angeles
- animal
- aniston
- announce
- announcement
- announcements
- anti
- antibiotics
- apps
- arch
- around
- arrives
- artist
- arts
- aspergers
- aspirin
- astigmatism
- atlanta
- attached
- attractions
- aunt
- average
- avoid
- away
- babies
- baby
- babys
- back
- backless
- backpack
- backpacks
- backyard
- bacterial
- bagel
- bags
- bahamas
- bake
- baked
- balances
- balloon
- balm
- banana
- bananas
- band
- bank
- barbie
- barrel
- bars
- based
- basket
- bassinet
- bassinets
- bath
- bathing
- bathroom
- bathtub
- bauer
- bday
- beach
- bean
- beans
- beast
- beat
- beautiful
- beckham
- bedding
- bedroom
- beds
- bedtime
- bedwetters
- beef
- beer
- before
- being
- belly
- belt
- belts
- benadryl
- benefits
- benign
- best
- better
- between
- bigger
- bilingual
- bingo
- bipolar
- birth
- birthday
- bismal
- bites
- biting
- bjorn
- black
- blank
- bleach
- bleeding
- blending
- blessing
- blindness
- blisters
- blocks
- blood
- blue
- blueberries
- blueberry
- board
- bobby
- bodies
- body
- boil
- bonnet
- book
- books
- booster
- boot
- born
- bottle
- bottles
- bottom
- bouncer
- bouncing
- bowel
- bowtie
- boys
- braid
- brand
- brands
- bras
- bread
- breast
- breastfed
- breastfeeding
- breathing
- brian
- britax
- britex
- bronchitis
- broth
- brother
- brown
- brunswick
- brussel
- bucket
- buffalo
- bugs
- bullet
- bumble
- bump
- bundt
- bunk
- burning
- busy
- butter
- butternut
- butterscotch
- button
- buttons
- cabinet
- cajun
- cake
- cakes
- calamine
- calendar
- california
- call
- calls
- calorie
- came
- cameron
- camp
- camper
- camps
- cards
- care
- carrier
- carrots
- cars
- cart
- casserole
- casseroles
- cast
- casting
- castle
- cauliflower
- cause
- causes
- cayman
- celebrity
- cell
- center
- centerpiece
- centerpieces
- cereal
- cervix
- cetaphil
- chair
- chairs
- chances
- changing
- chapter
- character
- chart
- charts
- checking
- checklist
- cheese
- cheesecake
- cheeses
- cheetos
- cherry
- chest
- chew
- chewable
- chicco
- chicken
- child
- childproof
- children
- childrens
- childs
- chin
- chinese
- chip
- chipotle
- chive
- chocolate
- choice
- chop
- chops
- chores
- christmas
- cinnamon
- circumference
- circumfrence
- circus
- city
- classes
- claus
- clean
- cleaner
- clear
- cloth
- clothes
- coat
- coats
- coconut
- coed
- cognitive
- cohosh
- cold
- colic
- colicky
- college
- color
- colorado
- colors
- colostrum
- come
- comotomo
- company
- conceive
- conceived
- concussion
- conflict
- congestion
- cons
- consequences
- consumer
- contest
- contigo
- control
- convertible
- cook
- cooker
- cookie
- cookies
- coping
- cornish
- correct
- corset
- corsets
- cost
- costume
- costumes
- cots
- cotton
- cough
- coughing
- could
- counter
- country
- couples
- course
- cousins
- cover
- covers
- cowboys
- cradle
- craft
- crafts
- cramping
- cramps
- cream
- creek
- crib
- cribs
- crisp
- crock
- crust
- crying
- cube
- cupcake
- cure
- curly
- curtains
- custard
- cute
- cutest
- cutlet
- cutting
- cycle
- daddy
- dads
- daily
- dark
- dating
- dawson
- daycare
- days
- dead
- deal
- deborah
- decor
- decorating
- decoration
- decorations
- deep
- delivery
- depression
- dermatitis
- desserts
- development
- diablo
- diaper
- diapers
- diarrhea
- didn
- diego
- difference
- digital
- dilated
- dilating
- discharge
- discipline
- discovery
- disney
- disorder
- disposable
- distance
- divorce
- divorcing
- dockatot
- does
- doesn
- dogs
- doll
- dollar
- dolls
- door
- dorel
- dosage
- down
- drawer
- drawing
- drbrown
- dream
- dreaming
- dress
- dresses
- dressing
- drinks
- drip
- drooling
- drop
- drops
- drowsy
- duck
- during
- early
- ears
- earths
- easter
- easy
- eczema
- eddie
- edison
- educational
- effective
- effects
- eggplant
- eggs
- eight
- electric
- elmo
- elves
- embrace
- embryo
- emilee
- enfamil
- english
- enlarged
- epidural
- episode
- ergo
- essential
- eucerin
- evansville
- evenflo
- evenflow
- event
- events
- examples
- excedrin
- exercise
- exercises
- expect
- expecting
- expert
- experts
- face
- facing
- factory
- fail
- fairy
- fall
- falls
- families
- family
- farmer
- fashioned
- fast
- father
- fathers
- favor
- favors
- feeder
- feeding
- feeling
- feels
- feet
- fertility
- fever
- fibroids
- fiesta
- figures
- fill
- filled
- filling
- find
- fine
- fingers
- fins
- first
- fisher
- flank
- flash
- float
- flonase
- floor
- flops
- fluttery
- folic
- food
- foods
- football
- foreign
- forever
- formula
- foster
- four
- freddie
- free
- french
- frequent
- friday
- fried
- friendly
- friends
- friendship
- from
- fruit
- funny
- furniture
- fussiness
- fussy
- gain
- gaines
- gaining
- game
- games
- gayness
- gear
- gender
- george
- gerbils
- getting
- ghost
- gift
- gifted
- gifts
- girdle
- girls
- give
- glass
- goats
- goddess
- goggles
- gold
- gonna
- good
- goody
- gown
- graco
- grade
- graders
- grandparents
- gras
- gravy
- grayson
- greek
- green
- grill
- grilled
- grip
- group
- grow
- growing
- growth
- guarantee
- guard
- gucci
- guess
- guide
- gummies
- guys
- habits
- hair
- halloween
- hamster
- hands
- hanukkah
- happy
- hard
- harlow
- harry
- have
- haves
- having
- head
- headbands
- heads
- healthy
- heart
- heartburn
- heater
- heavier
- helicopter
- hello
- helmet
- helmets
- help
- hemorrhoid
- henry
- high
- highback
- highest
- hilton
- history
- hold
- holding
- home
- homemade
- homeopathic
- homes
- honey
- hormones
- hospital
- hotels
- hour
- house
- houston
- huggies
- hunt
- hurts
- husband
- hybrid
- ideas
- image
- immediately
- important
- inch
- inclusive
- indian
- indiana
- indoor
- induce
- inducing
- infant
- infants
- infection
- infertility
- ingenuity
- ingredients
- inner
- insect
- insemination
- insert
- inspirational
- instructions
- instuments
- insurance
- introduce
- invitations
- iphone
- iron
- islands
- itch
- itchy
- ivan
- jack
- jackets
- jade
- jalapeno
- jammies
- jean
- jeans
- jessie
- joanna
- jokes
- joseph
- joys
- juice
- july
- jumping
- juvenile
- kardashian
- kate
- keep
- keeping
- kentucky
- keys
- kidneys
- kids
- kindergarten
- kiss
- kitchen
- kits
- kitten
- know
- labor
- labour
- lady
- language
- languages
- large
- laser
- last
- latch
- late
- laws
- learn
- learning
- leather
- left
- leftover
- legroom
- legs
- lemon
- lentil
- letter
- letters
- leukemia
- levels
- lice
- life
- lift
- ligation
- light
- lightest
- like
- lingerie
- lips
- list
- listening
- literature
- little
- lobster
- lock
- locks
- loin
- long
- look
- looks
- loompa
- lose
- losing
- loss
- lost
- lotion
- lotions
- love
- lower
- luck
- lullaby
- lulu
- lump
- lying
- lyme
- mache
- machine
- magestic
- magnetic
- majestic
- make
- maker
- makeup
- making
- male
- males
- manual
- many
- mardi
- mardis
- mark
- marks
- married
- mask
- massage
- maternity
- math
- maxi
- mccarthy
- meal
- mean
- meaning
- meatballs
- medela
- medicine
- medicines
- meijer
- meningitis
- menstrual
- meringue
- mermaid
- mesh
- messages
- messenger
- mexican
- miami
- michaels
- mickey
- micro
- microcephaly
- microwave
- middle
- mila
- mileage
- milestones
- milk
- minivan
- minnie
- minute
- miracle
- miralax
- mirena
- miscarriage
- miscarried
- mobile
- model
- modeling
- modesto
- moisturizer
- moldy
- molested
- mommy
- moms
- monitor
- monitors
- monofin
- monster
- month
- months
- morgan
- mosquito
- most
- mother
- mothers
- motor
- motrin
- mouse
- mouth
- movement
- movements
- movie
- movies
- moving
- much
- mucinex
- mucus
- multiplayer
- multiple
- munchkin
- museum
- music
- musical
- must
- myoclonus
- nachos
- nail
- name
- names
- nanny
- naples
- nasal
- nation
- native
- natural
- naturally
- naturals
- nausea
- nautical
- navy
- nebulizer
- neck
- necklace
- need
- needs
- negative
- neonatal
- nestle
- newborn
- newly
- night
- nine
- ninos
- noise
- noodle
- noodles
- nose
- notes
- nursery
- nurses
- nursing
- nutramigen
- oatmeal
- october
- odor
- offenders
- office
- oils
- older
- olds
- onesie
- onesies
- online
- oompa
- orajel
- orange
- oreo
- organic
- organizer
- origin
- orleans
- ornaments
- osprey
- ounce
- outback
- outfit
- outfits
- ovary
- over
- ovulate
- ovulating
- ovulation
- pack
- package
- pads
- pages
- pain
- paint
- pajamas
- palpitations
- pampers
- panini
- paninis
- pants
- paper
- papers
- parent
- parenthood
- parents
- park
- parks
- parmesan
- part
- parties
- party
- passes
- pasta
- patch
- patrick
- patrol
- patty
- pcos
- peach
- peaches
- peanut
- peanuts
- pediatrics
- pelvic
- people
- pepper
- period
- periods
- personalized
- philadelphia
- phone
- photo
- photos
- pics
- picture
- pictures
- piece
- pierce
- piercing
- piercings
- piggle
- piggy
- pill
- pillow
- pillows
- pills
- pillsbury
- pimples
- pineapple
- pink
- pinto
- pipe
- pizza
- place
- places
- plan
- plane
- plastic
- play
- playdate
- plus
- pockets
- poco
- poison
- pokemon
- polly
- pony
- pool
- pooping
- poppers
- popular
- pork
- portable
- portland
- position
- positive
- poster
- postpartum
- potato
- potatoes
- potty
- pouch
- pound
- pounds
- powder
- prediction
- predictor
- pregnancy
- pregnant
- premature
- prenatal
- prenatals
- preschool
- preschoolers
- present
- pressure
- prevent
- price
- prices
- prilosec
- princess
- printable
- prinze
- problems
- program
- programs
- projector
- prolapsed
- proof
- proofing
- pros
- protein
- provider
- puberty
- pull
- pulse
- pump
- pumpkin
- pumpkins
- pumps
- puree
- purse
- push
- queen
- questions
- quiz
- quotes
- race
- rail
- rails
- rainbow
- raising
- rash
- rate
- rates
- rattles
- reactive
- read
- reading
- real
- realistic
- reasons
- rebellious
- reborn
- recall
- recipe
- recipes
- reclining
- redness
- reflux
- regression
- relations
- relief
- relish
- remedies
- remote
- removal
- remove
- reoccuring
- repellent
- reports
- republic
- resemble
- resolutions
- resorts
- restaurants
- results
- reunion
- reveal
- revealing
- review
- reviews
- rhyme
- ribbon
- rice
- ride
- right
- ring
- rite
- ritzy
- roast
- roberta
- robes
- rock
- rocker
- roles
- roll
- roller
- rolls
- romance
- room
- rooms
- rotisserie
- round
- rubber
- ruby
- rugs
- rule
- running
- runny
- sacks
- safe
- safety
- sailor
- salad
- sale
- sales
- saline
- salmon
- salmonella
- same
- santa
- sauce
- sausage
- save
- saver
- scary
- scavenger
- schedule
- science
- sean
- season
- seat
- seats
- second
- section
- self
- sell
- selling
- sentences
- separation
- sets
- sexual
- shades
- shakes
- shampoo
- shape
- share
- sheets
- shell
- shells
- shield
- shirt
- shirts
- shoe
- shoelaces
- shoes
- shoot
- shopping
- shortcake
- shorts
- shot
- should
- shower
- showers
- side
- sign
- signs
- similac
- simple
- sing
- single
- sister
- sitting
- size
- sizes
- skeleton
- skin
- skip
- sleds
- sleep
- sleeper
- sleepers
- sleeping
- sling
- slings
- slow
- small
- smart
- smartphones
- smear
- snacks
- snapchat
- snow
- snowsuits
- soap
- soccer
- socks
- soft
- something
- songs
- soothing
- sore
- sound
- soup
- sour
- space
- spaces
- spanish
- special
- speech
- spot
- spotting
- sprouts
- squash
- stacking
- stage
- stages
- stand
- star
- starbucks
- start
- started
- state
- stationary
- steak
- step2
- stepchild
- steps
- stew
- stewart
- still
- sting
- stlouis
- stocking
- stomach
- stool
- stools
- stop
- stopping
- stories
- story
- storybook
- stove
- strap
- straps
- strawberry
- street
- strengthen
- stretch
- strips
- stroller
- strollers
- students
- study
- stuff
- stuffed
- stuffer
- stuffers
- style
- success
- sugar
- suit
- suitcases
- suits
- summer
- sunburn
- supplements
- supplies
- support
- supportive
- surgery
- surgical
- surprise
- surrogate
- surrogates
- swaddle
- swallowing
- sweet
- swim
- swimmable
- swimmers
- swimming
- swimsuit
- swimwear
- swing
- switch
- symbols
- symptom
- symptoms
- syndrome
- table
- tail
- tails
- take
- taking
- talented
- talk
- talking
- tall
- tamales
- tantrum
- tara
- target
- teach
- teachers
- teaching
- team
- teen
- teenage
- teenager
- teenagers
- teens
- teeth
- teething
- tell
- templates
- tenderness
- tens
- teriyaki
- test
- texas
- thai
- thank
- that
- their
- theme
- themed
- themes
- thigh
- things
- third
- this
- thomas
- three
- threw
- through
- throwing
- tied
- tier
- tight
- time
- tiny
- tips
- tissue
- title
- toast
- today
- toddler
- toddlers
- tofu
- toilet
- toilets
- tone
- tongue
- tonka
- tonsil
- tooth
- toys
- track
- train
- trainer
- training
- trampoline
- transverse
- trash
- travel
- tray
- treat
- treating
- treatment
- tree
- trek
- tribeca
- trick
- trimester
- truck
- true
- tubal
- tube
- tubes
- tuesdays
- tummy
- tums
- turkey
- turtle
- twice
- twin
- twinges
- twins
- tylenol
- types
- ultra
- ultrasound
- ultrasounds
- umbrella
- uncharted
- under
- underwear
- unique
- unisex
- unit
- urbini
- used
- using
- uterus
- vacation
- vacations
- vaginal
- valentine
- valentines
- vanilla
- vape
- varicose
- veins
- venues
- vera
- vest
- vests
- vicks
- video
- videos
- vinegar
- viral
- virgin
- viruses
- visit
- vitamin
- vitamins
- vivid
- vocabulary
- volunteering
- vomiting
- waist
- walgreens
- walk
- walker
- walkers
- walking
- wall
- wallpaper
- walmart
- walnut
- want
- warm
- warning
- warrior
- wars
- wash
- watch
- water
- wealth
- weaning
- wear
- weddings
- week
- weekend
- weeks
- weigh
- weight
- weighted
- weird
- what
- whats
- wheat
- wheel
- wheels
- when
- where
- while
- white
- whitening
- whole
- wide
- wife
- wiggle
- will
- windmills
- winning
- winter
- wipes
- wisdom
- with
- without
- woman
- women
- wood
- wooden
- word
- words
- work
- working
- workout
- world
- worse
- wrap
- wraps
- write
- xbox
- yankee
- yard
- year
- years
- yoga
- yogurt
- yoni
- young
- your
- zippers
- zyrtec

